Search in blog
Latest posts
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring chemical in hemp. By studying plants, the researchers identified more than 100 such phytochemical compounds, which are collectively called cannabinoids. Cannabidiol CBD and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are most prominent under typical volume conditions. CBD has no psychoactive properties compared to THC. Clinical studies indicate that CBD has broad medical applications, possibly larger than any other cannabinoid.
Each has a cannabinoid receptor system in the brain that contains a type 1 receptor (CB1) – mainly in the central and peripheral nervous system and a type 2 receptor (CB2) – primarily in the immune system. In addition to stimulating the production of natural cannabinoids, CBD inhibits an enzyme that metabolizes endocannabinoids. Although it has no affinity for primary receptors, CBD can increase receptor density and coupling efficiency, rather than binding to other receptors associated with - (adenosine (A2A), serotonin, pain perception, mood and inflammation. The cannabinoid receptor system plays an important role in maintaining a stable biological environment.
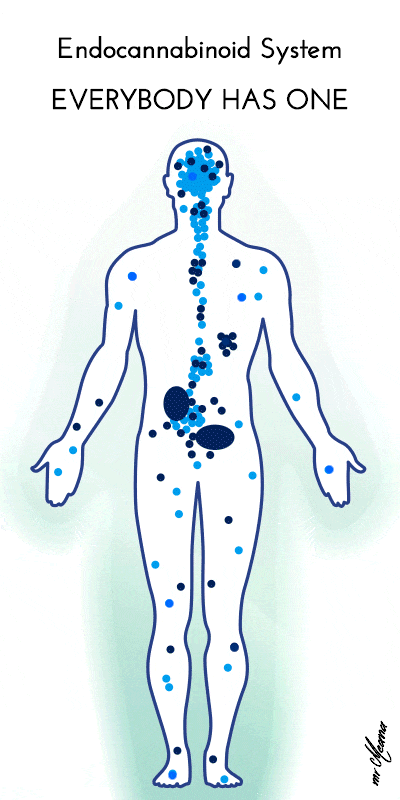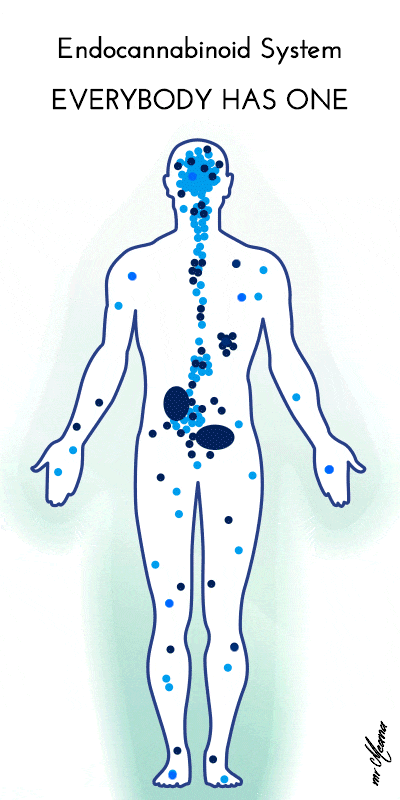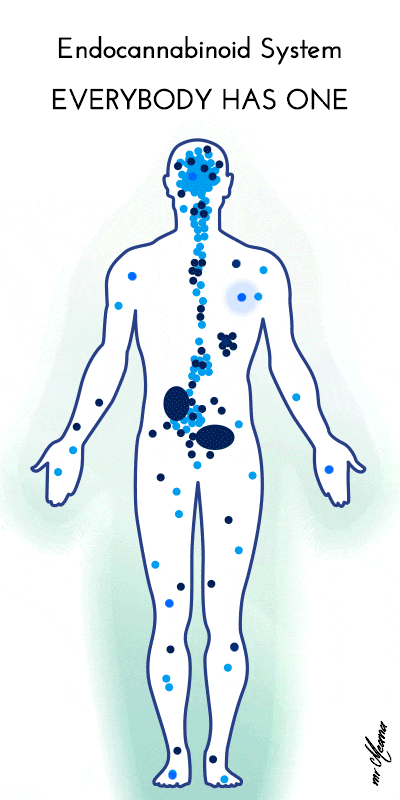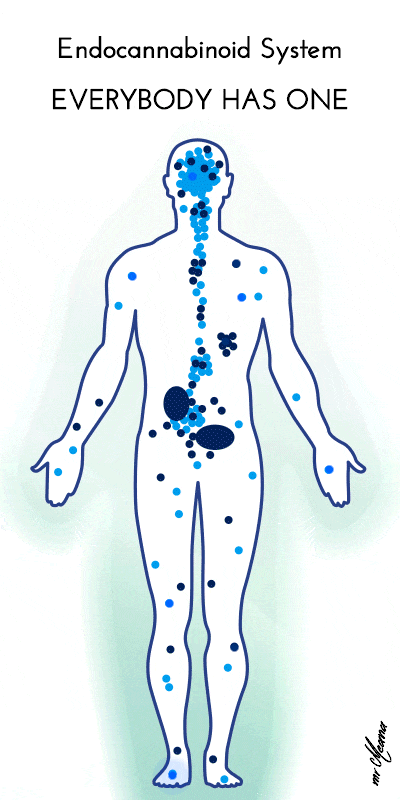
In the medical marijuana field, CBD presents itself as a huge and promising figure for a wide range of diseases and disorders, and its non-psychoactive profile allows for widespread use. As noted in the Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry in 2008, scientists established the chemical structure of CBD (in 1963), and this triggered a preliminary wave of medical research on its antiepileptic and sedative properties. In addition, Current Drug Safety in 2011 found that people tolerate CBD well, even with long-term use and high doses, and that CBD is non-toxic, with no negative effects associated with heart, blood pressure, body temperature, food intake, intestinal transit, or psychological functions.
To date, clinical trials involving CBD suggest that cannabinoids can be used in: anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, inflammation, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), neurodegenerative disorders, heart disease, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Crohn's disease and a debilitating form of epilepsy called Dravet syndrome. In addition, the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology noted that CBD has anti-cancer properties that interfere with "tumor neovascularization, cancer cell migration, adhesion, and invasion."
CBD oils and CBD pastes , in addition to the main active ingredient CBD, also contain other valuable cannabinoids that enhance its action - the most important of them are: CBC, CBG and CBN.
CBC – cannabichromenoic acid is a rare phytocannabinoid produced at a very early stage of cannabis flowering. This phytocannabinoid does not react with cannabinoid receptors, but acts as an antibiotic and antifungal agent. CBC also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, and animal tests also show its antidepressant properties.
CBG – cannabigerol is an analgesic and non-psychoactive compound – It is the third most commonly produced cannabinoid by plants after THC and CBD. Until recently, scientists did not pay as much attention to CBG as CBD and THC, but the latest research indicates that it is definitely worth taking an interest in this cannabinoid. CBG stands out from the main cannabinoids because it interacts with other receptors than those we can find in our endocannabinoid system. It is a powerful antibacterial agent that fights pathogens such as MRSA. Also interesting are its anti-cancer properties, which may be helpful in the fight against certain types of cancer, e.g. prostate and oral cavity.
CBN is not psychoactive in itself. Like CBG, it effectively fights infections caused by MRSA. Recent studies have shown that it can be effective in treating burns because it reduces the perceived sensitivity to heat.
Choose the proven and most popular CBD oil Endoca