Search in blog
Latest posts
It is well known that CBD does not produce psychoactive effects unlike THC. CBD is very well tolerated by our body even in very high doses and does not cause any intoxicating effects.
So why is THC psychoactive and CBD is not when both of these cannabinoids have a very similar chemical structure.
How one cannabinoid can change the effects of another.
The difference between THC and CBD is due to the effect on our endocannabinoid system (we distinguish mainly two CB1 and CB2 receptors - this system largely regulates our mental and physical health).
The psychoactive effects of THC are caused by the activation of CB1 receptors (they occur mainly in the brain), and CBD does not activate this receptor, so it does not cause psychoactive effects. Cannabidiol (CBD) binds to the CB2 receptor. These receptors are located primarily in the human immune system and are distributed throughout the body.
As shown in the figure below, the THC molecule is perfectly shaped to bind to CB1 receptors. When this happens, THC activates or stimulates these receptors, leading to euphoria, anxiety and possible short-term loss of consciousness. Scientists call THC a CB1 receptor agonist, which means that THC activates CB1 receptors. CBD, on the contrary, does not match CB1 receptors and is classified as a CB1 agonist antagonist, which means that it does not act directly on CB1 receptors, but rather acts on inhibiting the CB1-activating properties of cannabinoids such as THC.
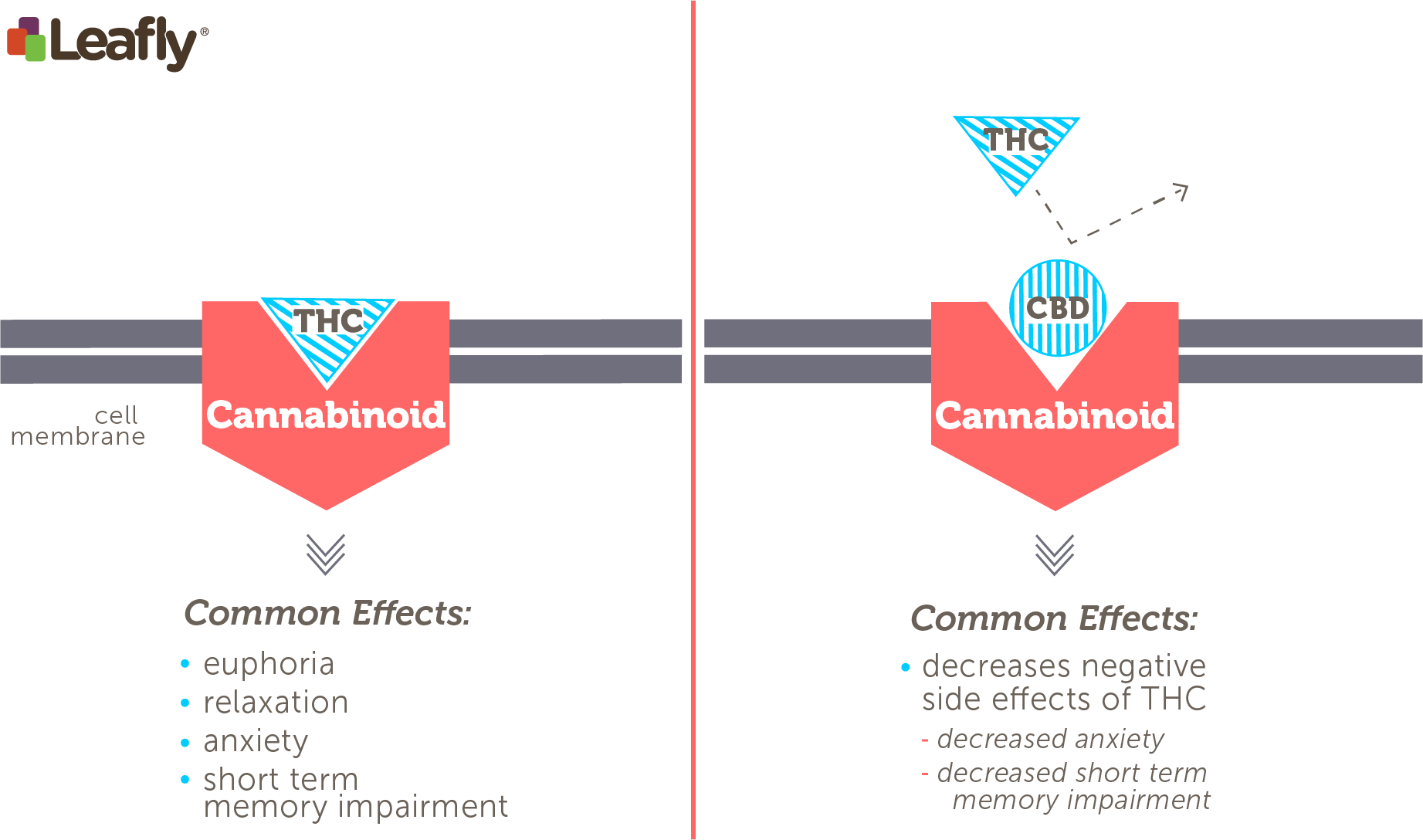
On the left, THC directly stimulates the CB1 receptor. This interaction underlies the main psychoactive effects of cannabis consumption. On the right, CBD reduces or "antagonizes" THC's ability to stimulate CB1 receptors. This leads to a reduction in some of the effects of THC particularly negative effects such as anxiety and short-term memory impairment.